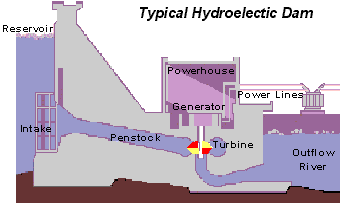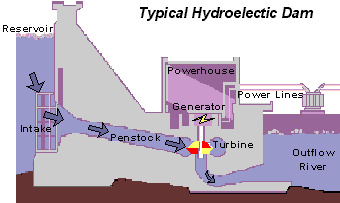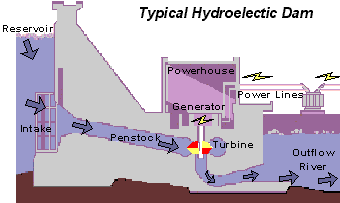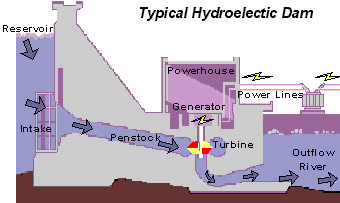
This is a picture of a more advanced Hydroelectric dam.The wheel in the mill example have been replaced with the mor efficient water turbines that are used to produce energy. The principles, however, are the same: water flows into the water turbines, which turns the shafts connected to a generator, creating energy
Hydropower uses the energy produced through moving water. This technology has literally been around for hundreds of years and, although our current methods and technology have improved the process and efficiency greatly, the same underlying principles are employed.
So how does HydroPower work?
Perhaps you remember how the Water Cycle – the continuous movement of water above and below the Earth’s surface – works. Water from the ocean evaporates and is released into the atmosphere, forming clouds as it cools. The clouds then travel inland and produce precipitation in the forms of rain and snow. Over time this precipitation creates streams and rivers that lead back to the ocean – starting the process over again. This water that is moving downstream picks up tons of force on its way down, which is the energy we employ when we speak about water power.
How do we Harness this Energy?
One example of how the power of water is harnessed to produce usable energy is with the simple water-powered mill wheel. The wheel uses water diverted from a stream to spin: the water comes in downstream and is diverted to the top of the wheel. It then flows into one of the buckets on the circumference of the wheel, which is dragged down by the force of gravity due to water, causing the wheel to spin. The wheel is connected to a shaft at the center (which is usually connected to some type of machinery that needs powering); as the wheel spins, low amounts of energy travel from the motion into the machine.
100% Green
This model is feasible anywhere there is moving water downstream. In addition, and this is the major benefit of using hydropower, nothing is depleted in this process! The water just keeps flowing downstream. This makes water a completely clean, renewable resource. In addition, some restrictions that other forms of renewables face do not pertain to hydro: hydropower energy production does not set with the sun, nor when the wind stops blowing. In addition, hydropower has long been much cheaper to produce than other renewables.

But how much power is produced?
Any moving water source has the potential to produce energy that can be converted into electricity; the extent of the energy produced is heavily dependent on the speed and intensity of the water movement. Add more moving water (or faster moving water) and you will produce more energy.
If you add pressure to this water, we are able to control and amplify the amount of energy that the water produces (pressurized water contains a lot of kinetic energy, as evidenced by a fire hose). Hydropower systems create this pressure either by the use of a dam, or within a pipe that runs downhill. The water behind the dam (or inside the pipe) creates pressure at the bottom, meaning we got more power from the flowing water.
Learn more different HydroPower Systems here